Axios 源码分析
Axios 源码分析
概念和API
- 概念:Axios 是一个基于 promise 的网络请求库,可以用于浏览器和 node.js。它是 isomorphic 的(即同一套代码可以运行在浏览器和node.js中)。在服务端它使用原生 node.js
http模块, 而在客户端 (浏览端) 则使用 XMLHttpRequests。 - 特性:
- 从浏览器创建 XMLHttpRequests
- 从 node.js 创建 http 请求
- 支持 Promise API
- 拦截请求和响应
- 转换请求和响应数据
- 取消请求
- 自动转换JSON数据
- 客户端支持防御XSRF:添加
xsrf头,默认为 cookie的编码值:{ 'X-XSRF-TOKEN':decodeURIComponent(document.cookie) }
- 常用 API:
axios.request(config)axios.get(url[, config])axios.delete(url[, config])axios.head(url[, config])axios.options(url[, config])axios.post(url[, data[, config]])axios.put(url[, data[, config]])axios.patch(url[, data[, config]])- 并发请求:
Promise.all() - 创建实例:
axios.create([config])
执行流程
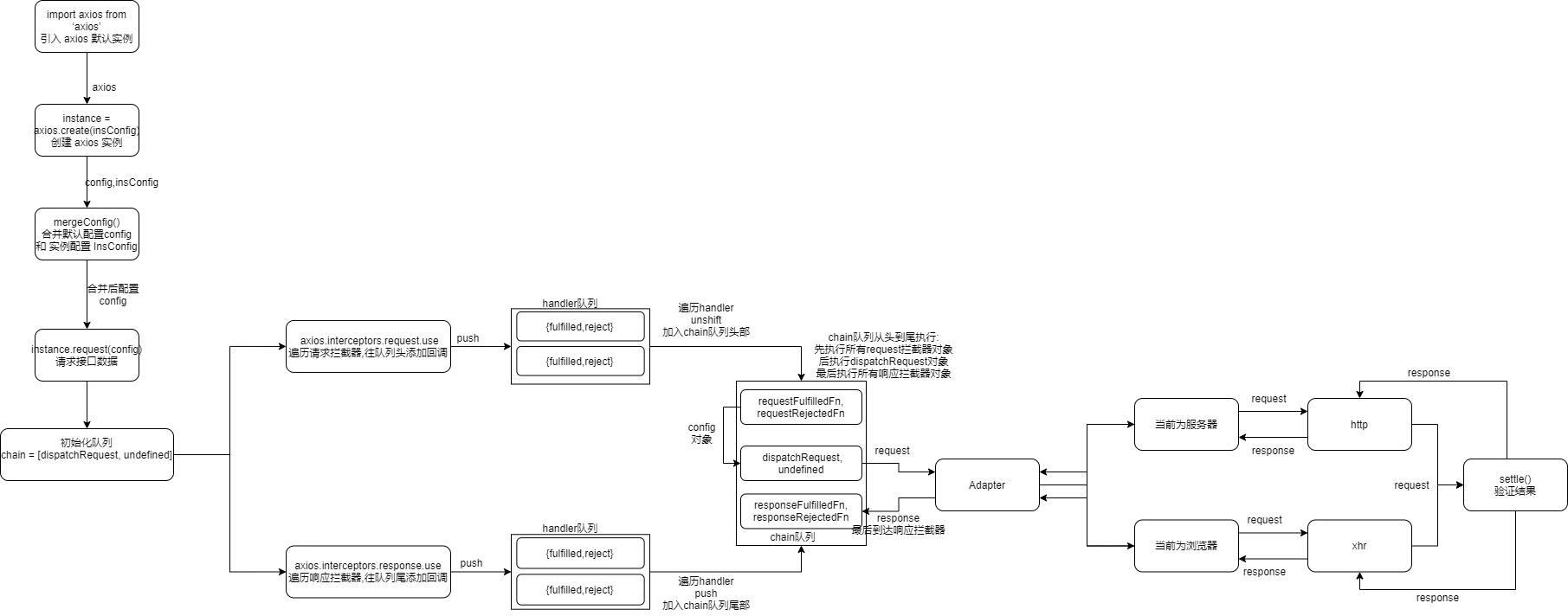
- axios 执行流程:
- 在实例化 axios 时,通过创建 axios 实例添加实例配置或修改默认配置
- 使用
axios.interceptors.request.use往 axios 实例中添加请求/响应拦截器 - 请求方法调用
request()方法 (axios的所有请求方法都是该方法的封装) - request() 方法中循环遍历 request interceptors 和 response interceptors,分别将 request 和 respose 拦截器实例加入 chain 队列头部和尾部,生成 [请求拦截器, dispatchRequest, 响应拦截器] 堆栈(使用了promise的链式调用)
- 循环遍历执行堆栈: 传入 config promise 对象 -> 执行所有 request handler -> dispatchRequest -> Adapter 对象 -> 根据环境调用 http/xhr 对象 -> settle() 方法验证结果 -> 执行所有响应拦截器对象 -> 前端/服务器。
- 前端/服务器使用axios请求方法发起请求 (axios.get, axios.post ...)
axios 实例
axios 实例使用方式:
- 第1种使用方式:
axios(option)
axios({
url,
method,
headers,
})
- 第2种使用方式:
axios(url[, option])
axios(url, {
method,
headers,
})
- 第3种使用方式(对于get、delete等方法):
axios[method](url[, option])
axios.get(url, {
headers,
})
- 第4种使用方式(对于post、put等方法):
axios[method](url[, data[, option]])
axios.post(url, data, {
headers,
})
- 第5种使用方式:
axios.request(option)
axios.request({
url,
method,
headers,
})
axios 默认实例
导入默认 axios 实例:
import axios from 'axios'axios 默认导出一个实例,修改了axios的默认配置,会影响所有的请求。
当在 a.js 文件中导入 axios 并修改默认配置后
// a.js import axios from 'axios' axios.defaults.baseURL = 'https://api.example.com';如果 b.js 中依赖 a.js 文件,在 b.js 中导入 axios,则 b.js 中的 axios 实例被 a.js 中影响
//b.js import axios from 'axios' console.log(axios.defaults.baseURL) //https://api.example.com解决方案: 每一个独立导入 axios 的文件中都创建新的 axios 实例,再修改配置。
源码分析:
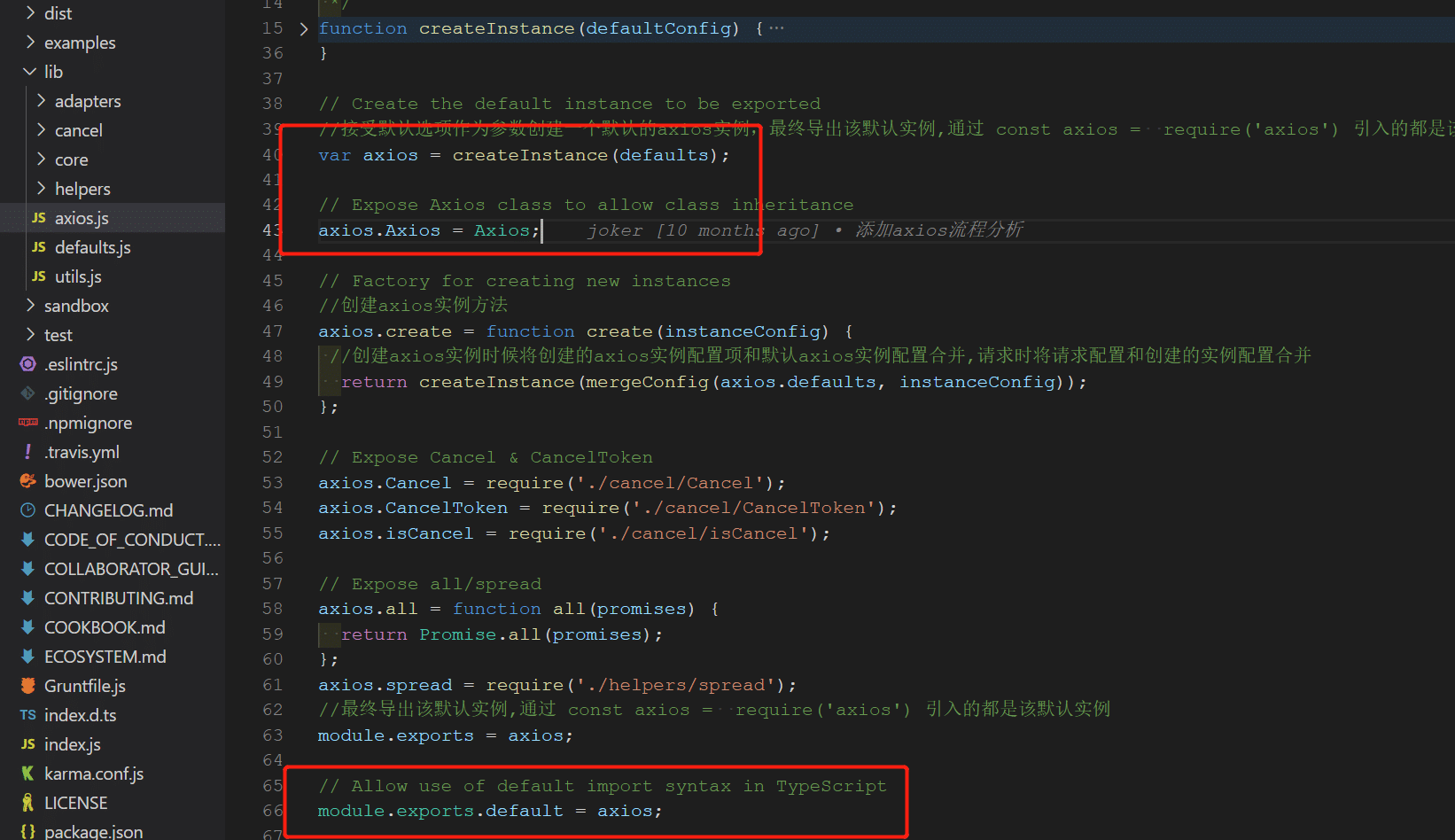
在入口文件中:使用默认配置创建一个 axios 实例并导出。定义在 lib/axios.js
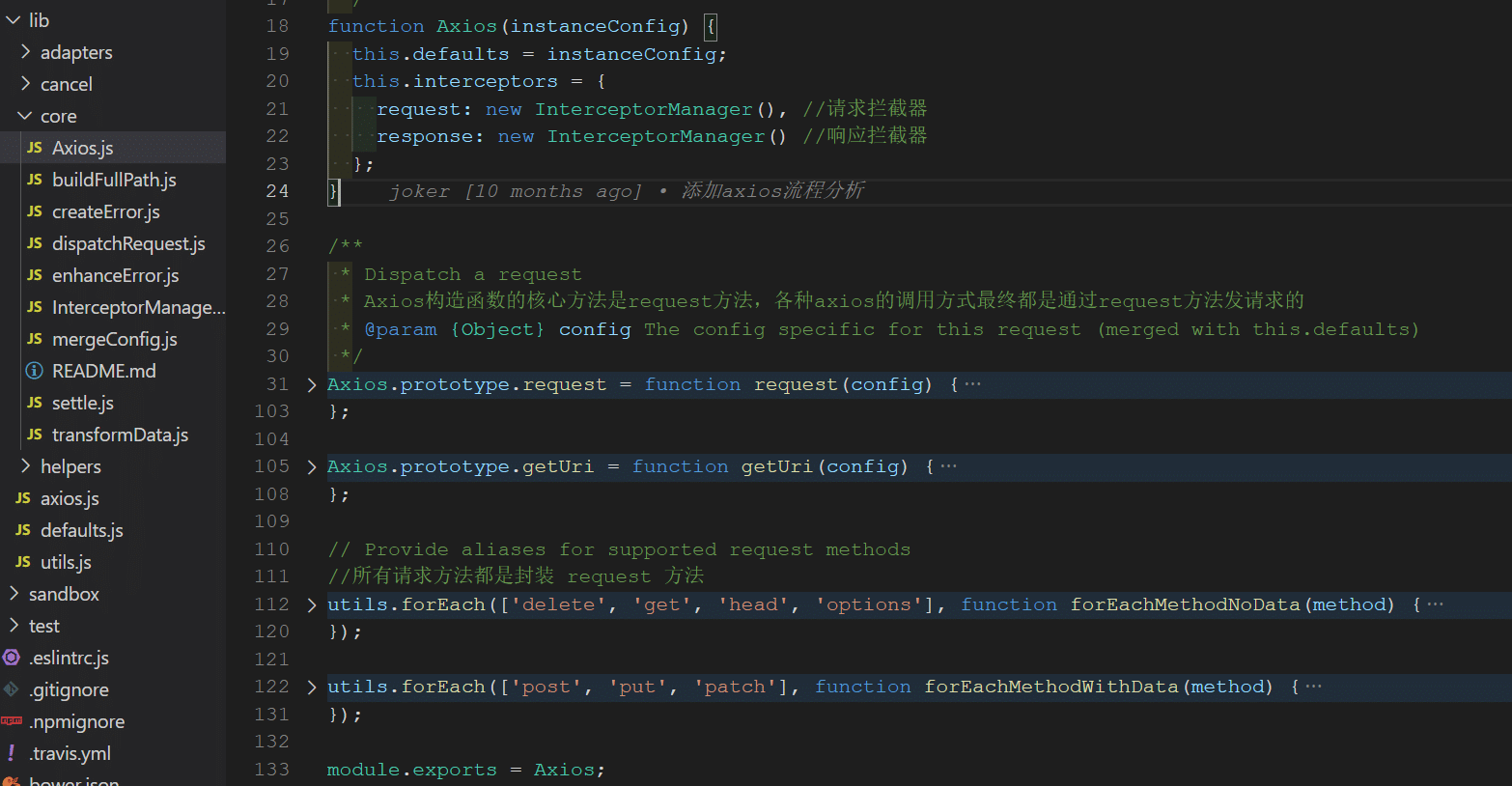
axios 实例对象定义默认配置和拦截器:定义在 lib/core/Axios.js
创建实例
API :
axios.create([config])const instance = axios.create({ baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/', timeout: 1000, headers: {'X-Custom-Header': 'foobar'} });
源码分析
axios.create([config])通过传入实例参数,合并默认配置和传入配置项,使用原型式继承创建新的实例。定义在 lib/axios.js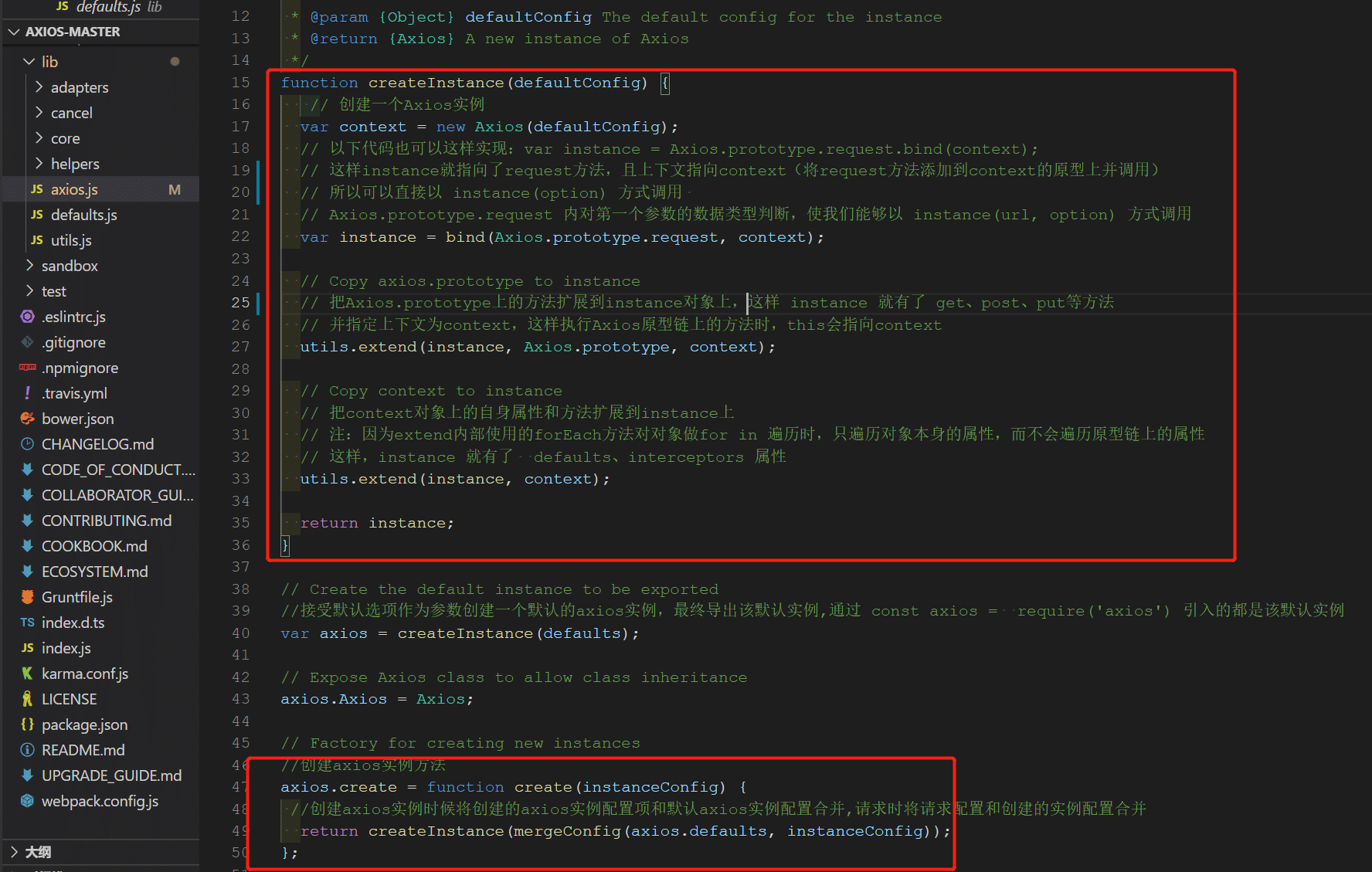
配置
axios 配置分为三类:
- axios 默认配置:创建默认 axios 实例的默认配置;
- axios 用户自定义实例配置: 通过
axios.create(config)时传入的配置; - 请求的
config配置: 在实例使用时传入的配置项。
默认配置
全局配置
axios.defaults自定义实例配置:
// 创建实例时配置默认值 const instance = axios.create({ baseURL: 'https://api.example.com' }); // 创建实例后修改默认值 instance.defaults请求配置选项。只有
url是必需的。如果没有指定method,请求将默认使用GET方法。{ // `url` 是用于请求的服务器 URL url: '/user', // `method` 是创建请求时使用的方法 method: 'get', // 默认值 // `baseURL` 将自动加在 `url` 前面,除非 `url` 是一个绝对 URL。 // 它可以通过设置一个 `baseURL` 便于为 axios 实例的方法传递相对 URL baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/', // `transformRequest` 允许在向服务器发送前,修改请求数据 // 它只能用与 'PUT', 'POST' 和 'PATCH' 这几个请求方法 // 数组中最后一个函数必须返回一个字符串, 一个Buffer实例,ArrayBuffer,FormData,或 Stream // 你可以修改请求头。 transformRequest: [function (data, headers) { // 对发送的 data 进行任意转换处理 return data; }], // `transformResponse` 在传递给 then/catch 前,允许修改响应数据 transformResponse: [function (data) { // 对接收的 data 进行任意转换处理 return data; }], // 自定义请求头 headers: {'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'}, // `params` 是与请求一起发送的 URL 参数 // 必须是一个简单对象或 URLSearchParams 对象 params: { ID: 12345 }, // `paramsSerializer`是可选方法,主要用于序列化`params` // (e.g. https://www.npmjs.com/package/qs, http://api.jquery.com/jquery.param/) paramsSerializer: function (params) { return Qs.stringify(params, {arrayFormat: 'brackets'}) }, // `data` 是作为请求体被发送的数据 // 仅适用 'PUT', 'POST', 'DELETE 和 'PATCH' 请求方法 // 在没有设置 `transformRequest` 时,则必须是以下类型之一: // - string, plain object, ArrayBuffer, ArrayBufferView, URLSearchParams // - 浏览器专属: FormData, File, Blob // - Node 专属: Stream, Buffer data: { firstName: 'Fred' }, // 发送请求体数据的可选语法 // 请求方式 post // 只有 value 会被发送,key 则不会 data: 'Country=Brasil&City=Belo Horizonte', // `timeout` 指定请求超时的毫秒数。 // 如果请求时间超过 `timeout` 的值,则请求会被中断 timeout: 1000, // 默认值是 `0` (永不超时) // `withCredentials` 表示跨域请求时是否需要使用凭证 withCredentials: false, // default // `adapter` 允许自定义处理请求,这使测试更加容易。 // 返回一个 promise 并提供一个有效的响应 (参见 lib/adapters/README.md)。 adapter: function (config) { /* ... */ }, // `auth` HTTP Basic Auth auth: { username: 'janedoe', password: 's00pers3cret' }, // `responseType` 表示浏览器将要响应的数据类型 // 选项包括: 'arraybuffer', 'document', 'json', 'text', 'stream' // 浏览器专属:'blob' responseType: 'json', // 默认值 // `responseEncoding` 表示用于解码响应的编码 (Node.js 专属) // 注意:忽略 `responseType` 的值为 'stream',或者是客户端请求 // Note: Ignored for `responseType` of 'stream' or client-side requests responseEncoding: 'utf8', // 默认值 // `xsrfCookieName` 是 xsrf token 的值,被用作 cookie 的名称 xsrfCookieName: 'XSRF-TOKEN', // 默认值 // `xsrfHeaderName` 是带有 xsrf token 值的http 请求头名称 xsrfHeaderName: 'X-XSRF-TOKEN', // 默认值 // `onUploadProgress` 允许为上传处理进度事件 // 浏览器专属 onUploadProgress: function (progressEvent) { // 处理原生进度事件 }, // `onDownloadProgress` 允许为下载处理进度事件 // 浏览器专属 onDownloadProgress: function (progressEvent) { // 处理原生进度事件 }, // `maxContentLength` 定义了node.js中允许的HTTP响应内容的最大字节数 maxContentLength: 2000, // `maxBodyLength`(仅Node)定义允许的http请求内容的最大字节数 maxBodyLength: 2000, // `validateStatus` 定义了对于给定的 HTTP状态码是 resolve 还是 reject promise。 // 如果 `validateStatus` 返回 `true` (或者设置为 `null` 或 `undefined`), // 则promise 将会 resolved,否则是 rejected。 validateStatus: function (status) { return status >= 200 && status < 300; // 默认值 }, // `maxRedirects` 定义了在node.js中要遵循的最大重定向数。 // 如果设置为0,则不会进行重定向 maxRedirects: 5, // 默认值 // `socketPath` 定义了在node.js中使用的UNIX套接字。 // e.g. '/var/run/docker.sock' 发送请求到 docker 守护进程。 // 只能指定 `socketPath` 或 `proxy` 。 // 若都指定,这使用 `socketPath` 。 socketPath: null, // default // `httpAgent` and `httpsAgent` define a custom agent to be used when performing http // and https requests, respectively, in node.js. This allows options to be added like // `keepAlive` that are not enabled by default. httpAgent: new http.Agent({ keepAlive: true }), httpsAgent: new https.Agent({ keepAlive: true }), // `proxy` 定义了代理服务器的主机名,端口和协议。 // 您可以使用常规的`http_proxy` 和 `https_proxy` 环境变量。 // 使用 `false` 可以禁用代理功能,同时环境变量也会被忽略。 // `auth`表示应使用HTTP Basic auth连接到代理,并且提供凭据。 // 这将设置一个 `Proxy-Authorization` 请求头,它会覆盖 `headers` 中已存在的自定义 `Proxy-Authorization` 请求头。 // 如果代理服务器使用 HTTPS,则必须设置 protocol 为`https` proxy: { protocol: 'https', host: '127.0.0.1', port: 9000, auth: { username: 'mikeymike', password: 'rapunz3l' } }, // see https://axios-http.com/docs/cancellation cancelToken: new CancelToken(function (cancel) { }), // `decompress` indicates whether or not the response body should be decompressed // automatically. If set to `true` will also remove the 'content-encoding' header // from the responses objects of all decompressed responses // - Node only (XHR cannot turn off decompression) decompress: true // 默认值 }
源码分析:
默认配置选项在创建 axios 默认实例时传入,定义在 lib/defaults.js
var defaults = { adapter: getDefaultAdapter(), transformRequest: [function transformRequest(data, headers) { normalizeHeaderName(headers, 'Accept'); normalizeHeaderName(headers, 'Content-Type'); if (utils.isFormData(data) || utils.isArrayBuffer(data) || utils.isBuffer(data) || utils.isStream(data) || utils.isFile(data) || utils.isBlob(data) ) { return data; } if (utils.isArrayBufferView(data)) { return data.buffer; } if (utils.isURLSearchParams(data)) { setContentTypeIfUnset(headers, 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8'); return data.toString(); } if (utils.isObject(data)) { setContentTypeIfUnset(headers, 'application/json;charset=utf-8'); return JSON.stringify(data); } return data; }], transformResponse: [function transformResponse(data) { /*eslint no-param-reassign:0*/ if (typeof data === 'string') { try { data = JSON.parse(data); } catch (e) { /* Ignore */ } } return data; }], /** * A timeout in milliseconds to abort a request. If set to 0 (default) a * timeout is not created. */ timeout: 0, xsrfCookieName: 'XSRF-TOKEN', xsrfHeaderName: 'X-XSRF-TOKEN', maxContentLength: -1, maxBodyLength: -1, validateStatus: function validateStatus(status) { return status >= 200 && status < 300; } }; defaults.headers = { common: { 'Accept': 'application/json, text/plain, */*' } }; utils.forEach(['delete', 'get', 'head'], function forEachMethodNoData(method) { defaults.headers[method] = {}; }); utils.forEach(['post', 'put', 'patch'], function forEachMethodWithData(method) { defaults.headers[method] = utils.merge(DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE); });
配置信息合并
请求配置信息合并策略:请求的
config参数 > 实例的defaults属性 > 库默认值。// 使用库提供的默认配置创建实例 // 此时超时配置的默认值是 `0` const instance = axios.create(); // 重写库的超时默认值 // 现在,所有使用此实例的请求都将等待2.5秒,然后才会超时 instance.defaults.timeout = 2500; // 重写此请求的超时时间,因为该请求需要很长时间 instance.get('/longRequest', { timeout: 5000 });
源码分析
在
axios.create(config)创建实例时候,将传入 配置项与默认配置项目通过mergeConfig合并,将实例配置覆盖默认配置。
在实际请求过程中,调用
axios.request()方法请求,该方法将实际请求配置与默认配置合并,用实际配置覆盖默认配置。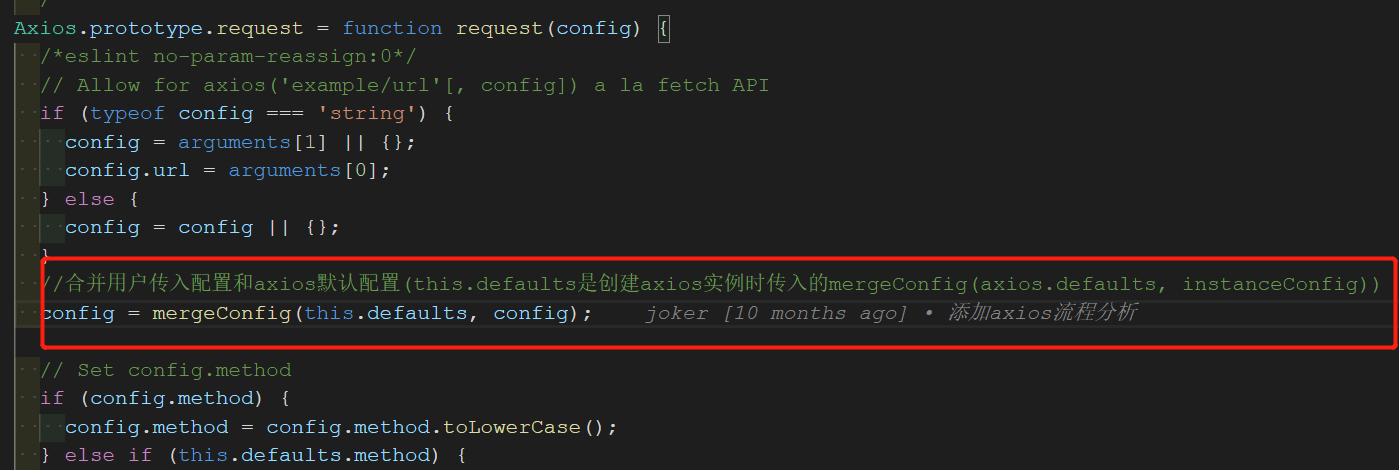
mergeConfig定义在lib/core/mergeConfig.jsmodule.exports = function mergeConfig(config1, config2) { // eslint-disable-next-line no-param-reassign config2 = config2 || {}; var config = {}; var valueFromConfig2Keys = ['url', 'method', 'data']; var mergeDeepPropertiesKeys = ['headers', 'auth', 'proxy', 'params']; var defaultToConfig2Keys = [ 'baseURL', 'transformRequest', 'transformResponse', 'paramsSerializer', 'timeout', 'timeoutMessage', 'withCredentials', 'adapter', 'responseType', 'xsrfCookieName', 'xsrfHeaderName', 'onUploadProgress', 'onDownloadProgress', 'decompress', 'maxContentLength', 'maxBodyLength', 'maxRedirects', 'transport', 'httpAgent', 'httpsAgent', 'cancelToken', 'socketPath', 'responseEncoding' ]; var directMergeKeys = ['validateStatus']; function getMergedValue(target, source) { if (utils.isPlainObject(target) && utils.isPlainObject(source)) { return utils.merge(target, source); } else if (utils.isPlainObject(source)) { return utils.merge({}, source); } else if (utils.isArray(source)) { return source.slice(); } return source; } function mergeDeepProperties(prop) { if (!utils.isUndefined(config2[prop])) { config[prop] = getMergedValue(config1[prop], config2[prop]); } else if (!utils.isUndefined(config1[prop])) { config[prop] = getMergedValue(undefined, config1[prop]); } } utils.forEach(valueFromConfig2Keys, function valueFromConfig2(prop) { if (!utils.isUndefined(config2[prop])) { config[prop] = getMergedValue(undefined, config2[prop]); } }); utils.forEach(mergeDeepPropertiesKeys, mergeDeepProperties); utils.forEach(defaultToConfig2Keys, function defaultToConfig2(prop) { if (!utils.isUndefined(config2[prop])) { config[prop] = getMergedValue(undefined, config2[prop]); } else if (!utils.isUndefined(config1[prop])) { config[prop] = getMergedValue(undefined, config1[prop]); } }); utils.forEach(directMergeKeys, function merge(prop) { if (prop in config2) { config[prop] = getMergedValue(config1[prop], config2[prop]); } else if (prop in config1) { config[prop] = getMergedValue(undefined, config1[prop]); } }); var axiosKeys = valueFromConfig2Keys .concat(mergeDeepPropertiesKeys) .concat(defaultToConfig2Keys) .concat(directMergeKeys); var otherKeys = Object .keys(config1) .concat(Object.keys(config2)) .filter(function filterAxiosKeys(key) { return axiosKeys.indexOf(key) === -1; }); utils.forEach(otherKeys, mergeDeepProperties); return config; };
响应信息
响应信息。
{ // `data` 由服务器提供的响应 data: {}, // `status` 来自服务器响应的 HTTP 状态码 status: 200, // `statusText` 来自服务器响应的 HTTP 状态信息 statusText: 'OK', // `headers` 是服务器响应头 // 所有的 header 名称都是小写,而且可以使用方括号语法访问 // 例如: `response.headers['content-type']` headers: {}, // `config` 是 `axios` 请求的配置信息 config: {}, // `request` 是生成此响应的请求 // 在node.js中它是最后一个ClientRequest实例 (in redirects), // 在浏览器中则是 XMLHttpRequest 实例 request: {} }
拦截器
添加拦截器:在请求或响应被 then 或 catch 处理前拦截它们。
// 添加请求拦截器 axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) { // 在发送请求之前做些什么 return config; }, function (error) { // 对请求错误做些什么 return Promise.reject(error); }); // 添加响应拦截器 axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) { // 2xx 范围内的状态码都会触发该函数。 // 对响应数据做点什么 return response; }, function (error) { // 超出 2xx 范围的状态码都会触发该函数。 // 对响应错误做点什么 return Promise.reject(error); });移除拦截器:
const myInterceptor = axios.interceptors.request.use(function () {/*...*/}); axios.interceptors.request.eject(myInterceptor);自定义的 axios 实例添加拦截器。
const instance = axios.create(); instance.interceptors.request.use(function () {/*...*/});
源码分析
axios 对象中拦截器的定义在 axios 实例中: lib/core/Axios.js
function Axios(instanceConfig) { this.defaults = instanceConfig; this.interceptors = { request: new InterceptorManager(), //请求拦截器 response: new InterceptorManager() //响应拦截器 }; }拦截器定义:拦截器实际是一个队列,use 方法往队列中添加拦截器。定义在lib/core/InterceptorManager.js
//拦截器对象 function InterceptorManager() { this.handlers = []; //拦截器堆栈 } /** * Add a new interceptor to the stack * 往拦截器堆栈中添加拦截器 * @param {Function} fulfilled The function to handle `then` for a `Promise` * @param {Function} rejected The function to handle `reject` for a `Promise` * * @return {Number} An ID used to remove interceptor later */ InterceptorManager.prototype.use = function use(fulfilled, rejected) { this.handlers.push({ fulfilled: fulfilled, rejected: rejected }); return this.handlers.length - 1; }; /** * Remove an interceptor from the stack * * @param {Number} id The ID that was returned by `use` */ InterceptorManager.prototype.eject = function eject(id) { if (this.handlers[id]) { this.handlers[id] = null; } }; /** * Iterate over all the registered interceptors * * This method is particularly useful for skipping over any * interceptors that may have become `null` calling `eject`. * * @param {Function} fn The function to call for each interceptor */ InterceptorManager.prototype.forEach = function forEach(fn) { utils.forEach(this.handlers, function forEachHandler(h) { if (h !== null) { fn(h); } }); };
请求方法
核心方法:request
Axios 构造函数的核心方法是 request 方法,各种 axios 的调用方式最终都是通过
axios.request(config)方法发请求的。axios.request(config)主要流程:- 合并请求配置;
- 创建循环队列,队列初始数据为请求适配器对象;
- 遍历请求拦截器队列,往循环队列头中添加请求拦截器;
- 遍历响应拦截器队列,往循环队列尾部添加响应拦截器;
- 串行执行异步循环队列;
- 注意:axios 请求是串行执行异步请求的,也就是说会按照请求入队列的逆序执行,某个请求的响应会等待上一个请求的响应返回后才能执行。
源码:定义在 lib/core/Axios.js
Axios.prototype.request = function request(config) { /*eslint no-param-reassign:0*/ // Allow for axios('example/url'[, config]) a la fetch API if (typeof config === 'string') { config = arguments[1] || {}; config.url = arguments[0]; } else { config = config || {}; } //合并用户传入配置和axios默认配置(this.defaults是创建axios实例时传入的mergeConfig(axios.defaults, instanceConfig)) config = mergeConfig(this.defaults, config); // Set config.method if (config.method) { config.method = config.method.toLowerCase(); } else if (this.defaults.method) { config.method = this.defaults.method.toLowerCase(); } else { config.method = 'get'; } // Hook up interceptors middleware //循环队列 var chain = [dispatchRequest, undefined]; // 将config对象当作参数传给Primise.resolve方法 var promise = Promise.resolve(config); //遍历所有请求拦截器,将所有请求拦截器添加到循环队列头部 this.interceptors.request.forEach(function unshiftRequestInterceptors(interceptor) { chain.unshift(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected); }); //遍历所有响应拦截器,将所有响应拦截器添加到循环队列尾部 this.interceptors.response.forEach(function pushResponseInterceptors(interceptor) { chain.push(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected); }); // 添加了拦截器后的chain数组大概会是这样的: // [ // requestFulfilledFn, requestRejectedFn, ..., // dispatchRequest, undefined, // responseFulfilledFn, responseRejectedFn, ...., // ] // config会按序通过 请求拦截器 - dispatchRequest方法 - 响应拦截器 while (chain.length) { // 串行执行循环队列 chain promise = promise.then(chain.shift(), chain.shift()); } return promise; };
模拟实现请求队列
//请求1
let req1 = function () {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
console.log('request1 start->')
setTimeout(function () {
resolve('request1->')
console.log('request1 end->')
}, 1000)
})
}
// 请求2
let req2 = function (data) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
console.log('request2 start->')
resolve(data + 'request2->')
console.log('request2 end->')
})
}
// 请求3
let req3 = function (data) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
console.log('request3 start->')
setTimeout(function () {
resolve(data + 'request3->')
console.log('request3 end->')
}, 500)
})
}
//响应1
let res1 = function () {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('get response1->')
resolve('response1 ->')
}, 1100)
})
}
//响应数据2
let res2 = function (data) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
console.log('get response2->')
resolve(data + 'response2->')
})
}
let res3 = function (data) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('get response3->')
resolve(data + 'response3->')
}, 500)
})
}
let chain = []
let requeseInter = [req1,req2,req3]
let responseInter = [res1,res2,res3]
requeseInter.forEach(p=>chain.unshift(p));
responseInter.forEach(p=>chain.push(p));
let promise = Promise.resolve({})
while(chain.length){
promise = promise.then(chain.shift());
}
console.log(promise)
执行结果: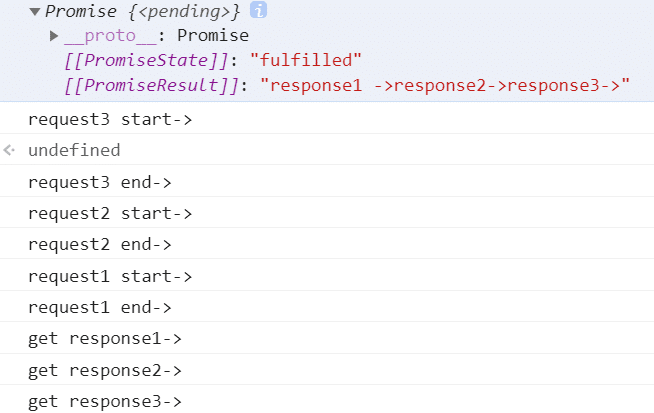
其他请求方法
Axios 实例就是一个 axios 应用,其他方法都是对 Axios 内容的扩展,axios 构造函数的核心方法是 request 方法,各种 axios 的调用方式最终都是通过 request 方法发请求的。
axios.get(url[, config])axios.delete(url[, config])axios.head(url[, config])axios.options(url[, config])axios.post(url[, data[, config]])axios.put(url[, data[, config]])axios.patch(url[, data[, config]])
axios.get(url[, config])axios.delete(url[, config])axios.head(url[, config])axios.options(url[, config]).axios.post(url[, data[, config]])axios.put(url[, data[, config]])axios.patch(url[, data[, config]])
实现:遍历方法名,合并配置项目参数,返回 reques 方法。定义在 lib/core/Axios.js
// Provide aliases for supported request methods //所有请求方法都是封装 request 方法 utils.forEach(['delete', 'get', 'head', 'options'], function forEachMethodNoData(method) { /*eslint func-names:0*/ Axios.prototype[method] = function(url, config) { return this.request(mergeConfig(config || {}, { method: method, url: url })); }; }); utils.forEach(['post', 'put', 'patch'], function forEachMethodWithData(method) { /*eslint func-names:0*/ Axios.prototype[method] = function(url, data, config) { return this.request(mergeConfig(config || {}, { method: method, url: url, data: data })); }; });
发送请求
在 axios 中请求方法都是通过 axios.request 完成,上面分析过:request 中初始队列中使用
dispatchRequest方法,当拦截器队列中所有请求被串行执行完成后,执行dispatchRequest方法,最后执行响应拦截器。dispatchRequest方法:定义在/lib/core/dispatchRequest.js- 检查是否取消,若取消则抛出请求取消错误;
- 处理请求配置 config、转换请求格式;
- 使用适配器发送请求;
- 最后处理响应数据:首先检查请求是否已经取消,已经取消抛出请求取消错误;否则转换响应数据并返回。
/** * Dispatch a request to the server using the configured adapter. * 使用配置的适配器发送请求 * @param {object} config The config that is to be used for the request * @returns {Promise} The Promise to be fulfilled */ module.exports = function dispatchRequest(config) { throwIfCancellationRequested(config); //如果已请求取消,抛出' Cancel '。 // Ensure headers exist config.headers = config.headers || {}; // Transform request data //transformRequest 是在配置请求配置时候传入的自定义转换方法,在此处请求前转换。 config.data = transformData( config.data, config.headers, config.transformRequest ); // Flatten headers config.headers = utils.merge( config.headers.common || {}, config.headers[config.method] || {}, config.headers ); utils.forEach( ['delete', 'get', 'head', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'common'], function cleanHeaderConfig(method) { delete config.headers[method]; } ); var adapter = config.adapter || defaults.adapter; return adapter(config).then(function onAdapterResolution(response) { //响应成功处理方法 throwIfCancellationRequested(config); // Transform response data // response.data = transformData( response.data, response.headers, config.transformResponse ); return response; }, function onAdapterRejection(reason) { //响应失败处理方法 if (!isCancel(reason)) { throwIfCancellationRequested(config); // Transform response data if (reason && reason.response) { reason.response.data = transformData( reason.response.data, reason.response.headers, config.transformResponse ); } } return Promise.reject(reason); }); };
适配器
- Axios 是一个基于 promise 的网络请求库,可以用于浏览器和 node.js。它是 isomorphic 的(即同一套代码可以运行在浏览器和node.js中)。在服务端它使用原生 node.js
http模块, 而在客户端 (浏览端) 则使用 XMLHttpRequests。 - isomorphic 的实现,使用适配器设计模式来屏蔽平台的差异性,让使用者可以在浏览器端和 NodeJS 环境中使用同一套 API 发起 http 请求。
- http请求适配器就是一个方法,在axios项目里,http请求适配器主要指两种:XHR 和 HTTP。
- XHR:核心是浏览器端的XMLHttpRequest对象。
- HTTP:核心是 node 的 http/https 的 request 方法。
源码分析:
添加默认是适配器:
在默认导入 axios 实例时,axios 使用默配置创建 axios 实例。
在 lib/defaults.js默认配置中使用
getDefaultAdapter获取默认 adapter 适配器。getDefaultAdapter方法:判断XMLHttpRequest和process对象,获取 xhr/http 适配器。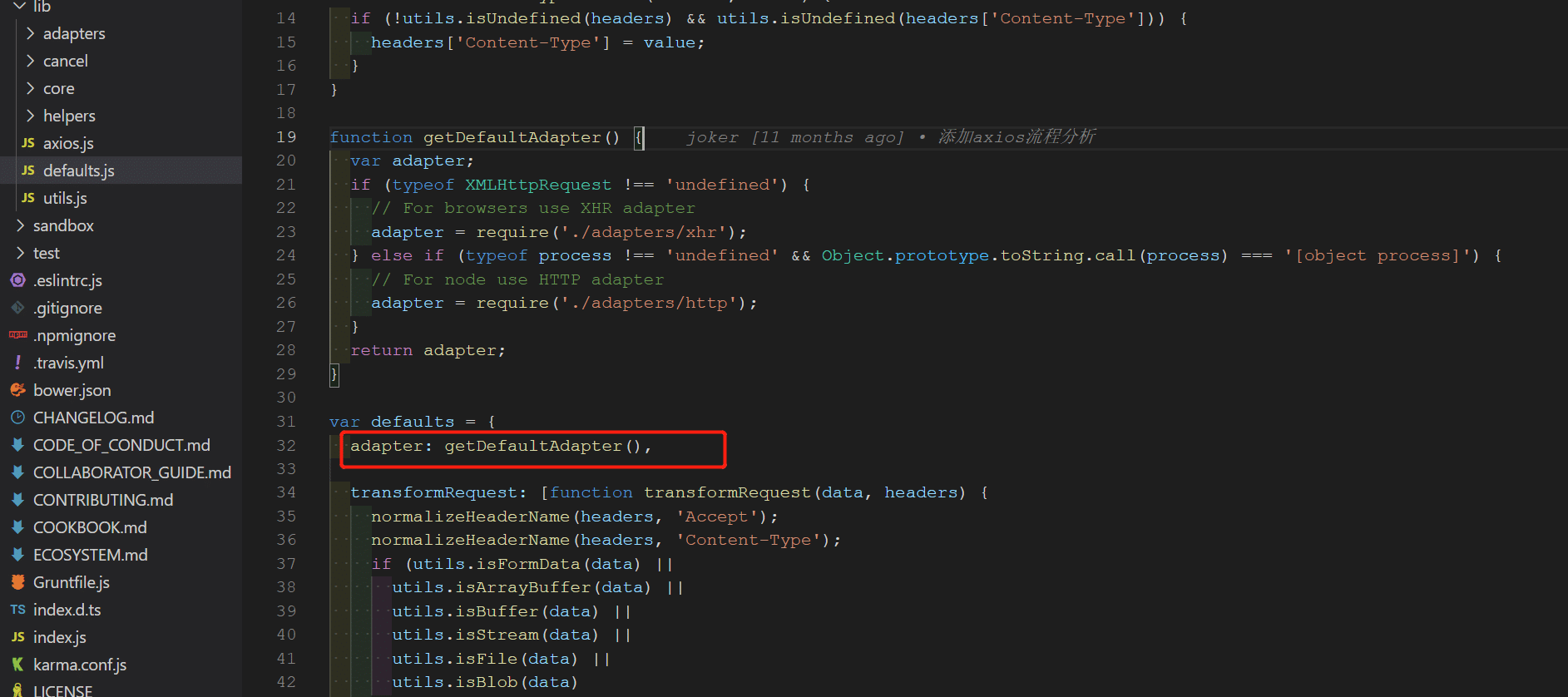
使用适配器:
- 在上节中分析到: request 串行请求遍历拦截器 ->
dispatchRequest返送请求 -> 返回适配器。流程中dispatchRequest方法调用适配器。
- 在上节中分析到: request 串行请求遍历拦截器 ->
XHR 适配器: 创建
XMLHttpReques对象,添加请求结果处理、中断超时处理、错误处理方法,进行参数转换、xsrf 处理、请求取消处理等。定义在lib/adapters/xhr.jsHTTP 适配器: 参数、配置处理,根据配置创建 http/https/httpsFollow/httpFollow 对象,发送请求。
适配器中结果返回后,统一调用 sette() 方法进行结果验证。
settle 方法: 使用配置参数中自定义验证方法验证结果。
// /lib/core/settle.js module.exports = function settle(resolve, reject, response) { var validateStatus = response.config.validateStatus; if (!validateStatus || validateStatus(response.status)) { resolve(response); } else { reject(createError( 'Request failed with status code ' + response.status, response.config, null, response.request, response )); } };
取消请求
使用 cancel token 取消一个请求:Axios 的 cancel token API 是基于被撤销 cancelable promises proposal。
可以使用同一个 cancel token 取消多个请求。
取消请求方式:
传递一个 executor 函数到
CancelToken的构造函数来创建一个 cancel token:const CancelToken = axios.CancelToken; let cancel; axios.get('/user/12345', { cancelToken: new CancelToken(function executor(c) { // executor 函数接收一个 cancel 函数作为参数,调用 cancel 函数可以取消请求操作 cancel = c; }) }); // 取消请求 cancel();使用
CancelToken.source工厂方法创建一个 cancel token :const CancelToken = axios.CancelToken; const source = CancelToken.source(); axios.get('/user/12345', { cancelToken: source.token }).catch(function (thrown) { if (axios.isCancel(thrown)) { console.log('Request canceled', thrown.message); } else { // 处理错误 } }); axios.post('/user/12345', { name: 'new name' }, { cancelToken: source.token }) // 取消请求(message 参数是可选的) source.cancel('Operation canceled by the user.');
源码分析:
取消请求判断时机:在 创建 axios实例 -> 合并配置 -> 添加拦截器 -> 遍历拦截器队列 -> dispatchRequest 分发请求前,检查请求是否取消 -> 适配器发送请求时检查是否取消请求 -> 适配器中响应数据返回到
dispatchRequest方法后,再次检查请求是否取消。因此一共经过三次请求取消检查。- 第一次取消检查:dispatchRequest 分发请求前,检查请求是否取消。在/lib/core/dispatchRequest.js。
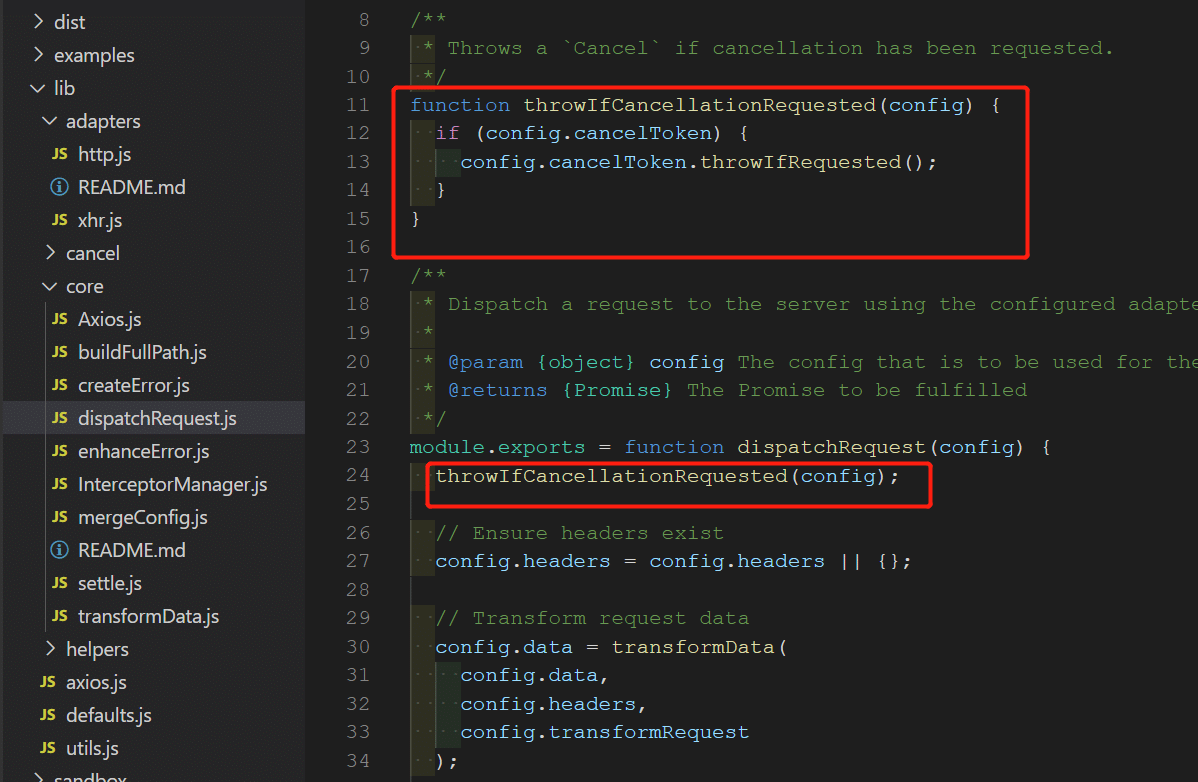
第二次取消检查:适配器发送请求时检查是否取消请求。
- XHR 适配器中:
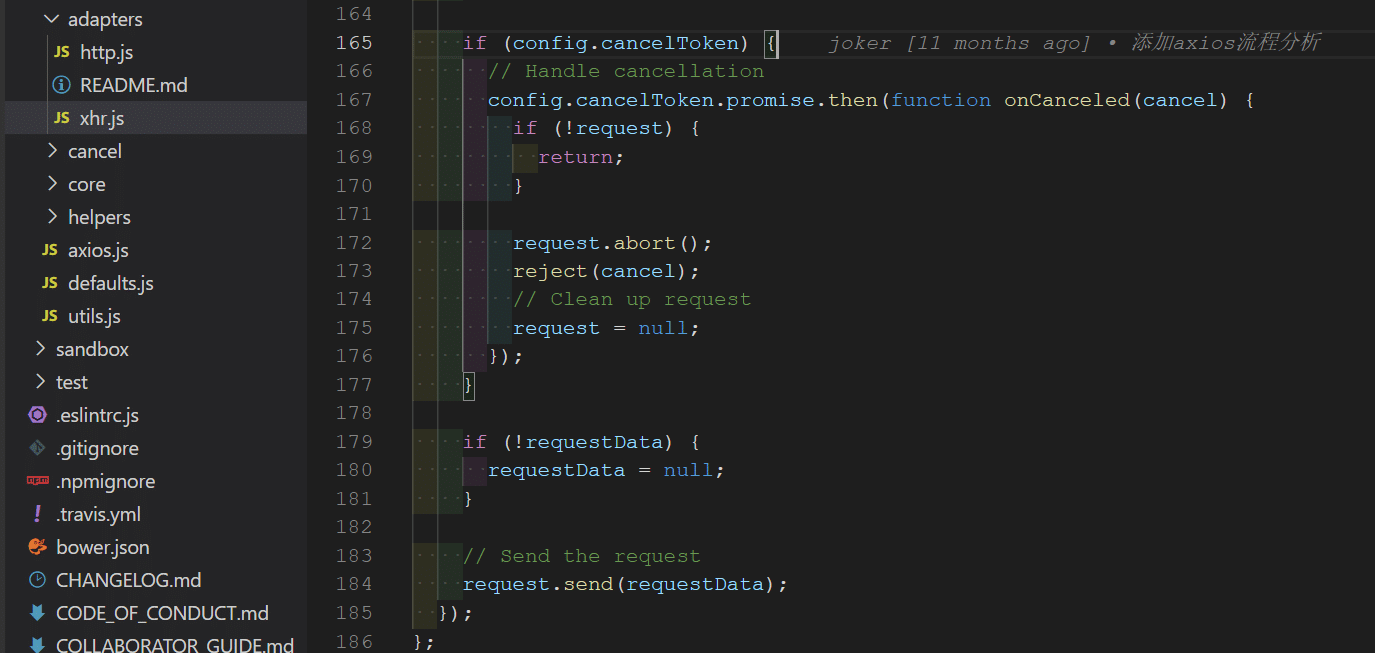
- HTTP 是配器中:
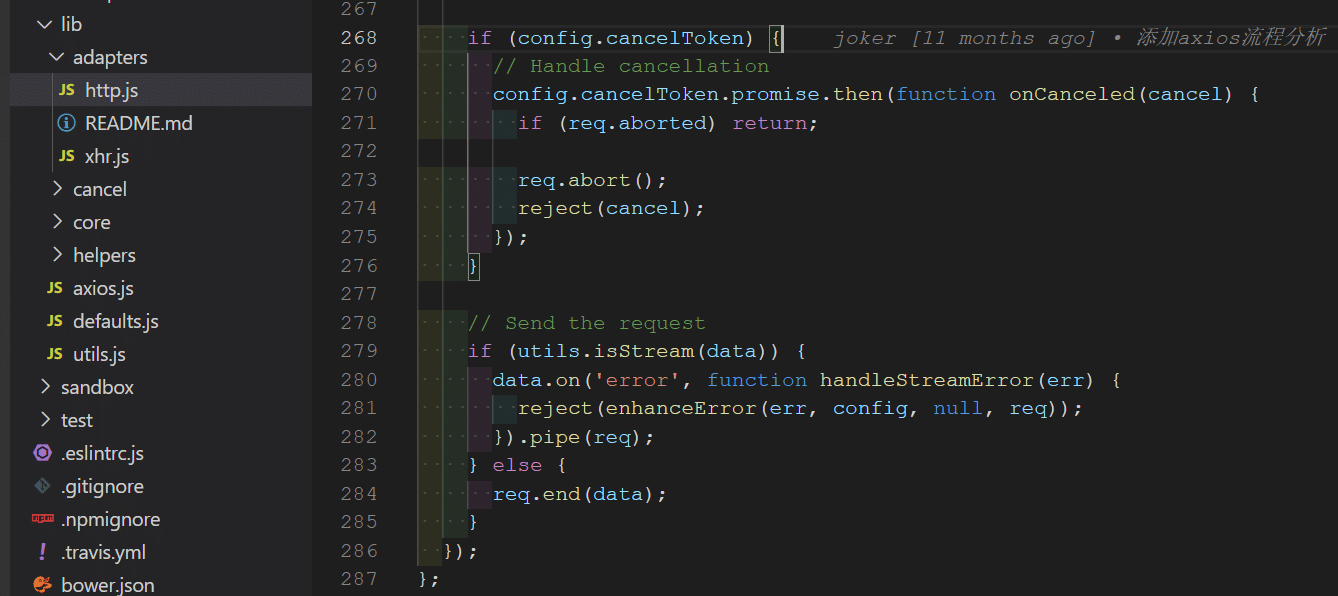
- XHR 适配器中:
第三次取消检查:适配器中响应数据返回到
dispatchRequest方法后,再次检查请求是否取消。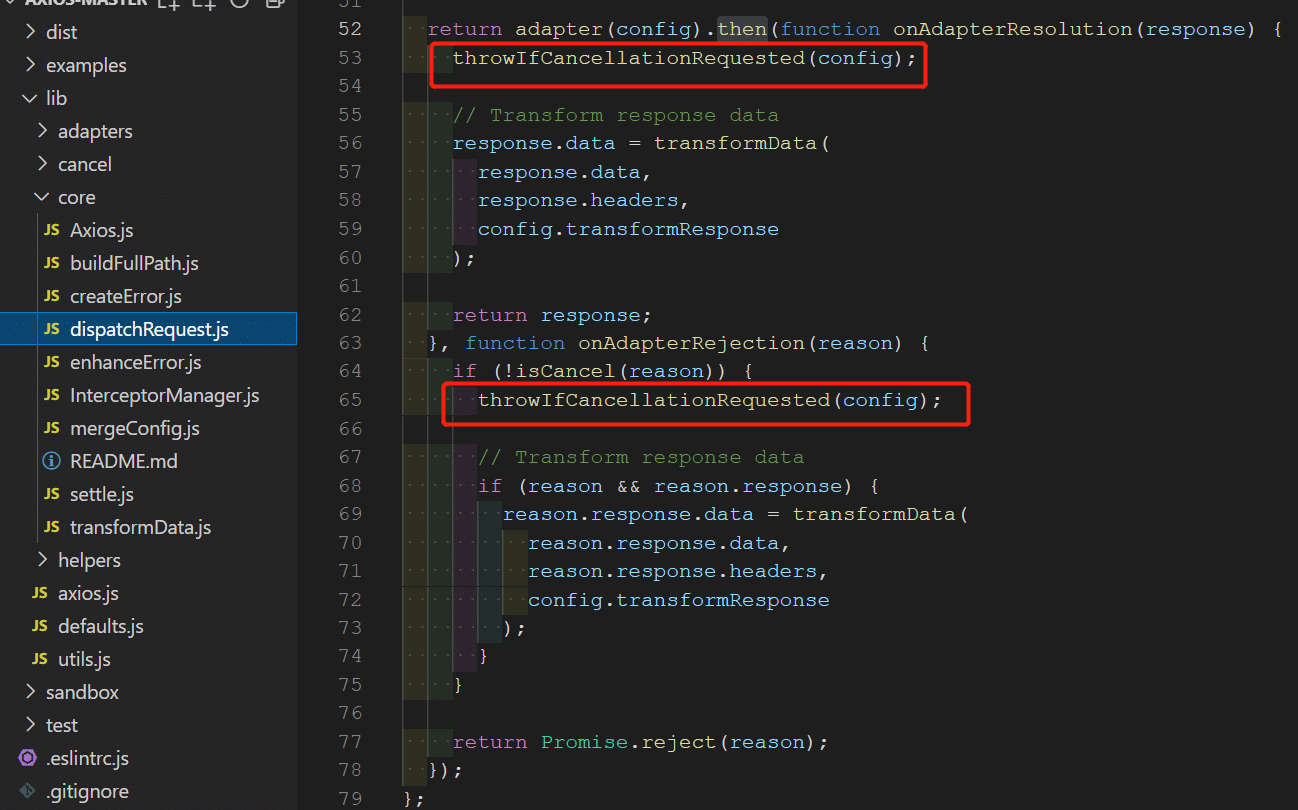
使用 cancel token 有两种不同使用方式:
传递一个 executor 函数到
CancelToken的构造函数来创建一个 cancel token。CancelToken的构造函数:/** * A `CancelToken` is an object that can be used to request cancellation of an operation. * 一个可以取消请求操作的 CancelToken 对象 * @class * @param {Function} executor The executor function. 参数为执行器函数 */ function CancelToken(executor) { if (typeof executor !== 'function') { //执行器必须为函数 throw new TypeError('executor must be a function.'); } var resolvePromise; this.promise = new Promise(function promiseExecutor(resolve) { resolvePromise = resolve; }); var token = this; // 保存对象上下文 executor(function cancel(message) { //执行执行器方法,传入 cancel 方法作为 执行器回调 if (token.reason) { // Cancellation has already been requested return; } token.reason = new Cancel(message); //创建 cancel 对象 resolvePromise(token.reason); //返回 cancel 对象作为回调 }); }Cancle对象定义:只有一个 message 参数,表示取消信息,创建后__CANCEL__变量为 true,用于判断请求是否已经取消。/** * A `Cancel` is an object that is thrown when an operation is canceled. * * @class * @param {string=} message The message. */ function Cancel(message) { this.message = message; } Cancel.prototype.toString = function toString() { return 'Cancel' + (this.message ? ': ' + this.message : ''); }; Cancel.prototype.__CANCEL__ = true;//用于判断请求是否已经取消。判断请求是否取消:
isCancel(),判断 Cancel 对象原型中__CANCEL__变量。 当调用执行器的cancel()方法后,会创建Cancel对象,该对象__CANCEL__变量为 true,表示已经取消请求。module.exports = function isCancel(value) { return !!(value && value.__CANCEL__); };
使用
CancelToken.source工厂方法创建一个 cancel token 过程:CancelToken.source()方法返回 CancelToken 对象和该对象的取消方法。CancelToken.source()源码:/** * Returns an object that contains a new `CancelToken` and a function that, when called, * cancels the `CancelToken`. * 返回一个 CancelToken 对象 和 cancel 方法 */ CancelToken.source = function source() { var cancel; // token 为 CancelToken 实例,传入默认执行器,使用 cancel 保存执行器的取消方法 var token = new CancelToken(function executor(c) { cancel = c; }); return { token: token, cancel: cancel }; };
错误处理
错误处理:
catch()、validateStatus配置选项、axios.get('/user/12345') .catch(function (error) { if (error.response) { // 请求成功发出且服务器也响应了状态码,但状态代码超出了 2xx 的范围 console.log(error.response.data); console.log(error.response.status); console.log(error.response.headers); } else if (error.request) { // 请求已经成功发起,但没有收到响应 // `error.request` 在浏览器中是 XMLHttpRequest 的实例, // 而在node.js中是 http.ClientRequest 的实例 console.log(error.request); } else { // 发送请求时出了点问题 console.log('Error', error.message); } console.log(error.config); });使用
validateStatus配置选项,可以自定义抛出错误的 HTTP code。axios.get('/user/12345', { validateStatus: function (status) { return status < 500; // 处理状态码小于500的情况 } })使用
toJSON可以获取更多关于HTTP错误的信息。axios.get('/user/12345') .catch(function (error) { console.log(error.toJSON()); });
请求体编码
默认情况下,axios将 JavaScript 对象序列化为 JSON 。
要以application/x-www-form-urlencoded格式发送数据,您可以使用以下选项之一。
浏览器
在浏览器中,可以使用URLSearchParams API,如下所示:
const params = new URLSearchParams();
params.append('param1', 'value1');
params.append('param2', 'value2');
axios.post('/foo', params);
请注意,不是所有的浏览器(参见 caniuse.com)都支持
URLSearchParams,但是可以使用polyfill (确保 polyfill 全局环境)
或者, 您可以使用qs 库编码数据:
const qs = require('qs');
axios.post('/foo', qs.stringify({ 'bar': 123 }));
或者用另一种方式 (ES6),
import qs from 'qs';
const data = { 'bar': 123 };
const options = {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'content-type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' },
data: qs.stringify(data),
url,
};
axios(options);
Node.js
- Query string
在 node.js 中, 可以使用 querystring 模块,如下所示:
const querystring = require('querystring');
axios.post('http://something.com/', querystring.stringify({ foo: 'bar' }));
或者从'url module'中使用'URLSearchParams',如下所示:
const url = require('url');
const params = new url.URLSearchParams({ foo: 'bar' });
axios.post('http://something.com/', params.toString());
您也可以使用 qs 库。
注意
如果需要对嵌套对象进行字符串化处理,则最好使用 qs 库,因为 querystring 方法在该用例中存在已知问题(https://github.com/nodejs/node-v0.x-archive/issues/1665)。
Form data
在 node.js, 您可以使用 form-data 库,如下所示:
const FormData = require('form-data');
const form = new FormData();
form.append('my_field', 'my value');
form.append('my_buffer', new Buffer(10));
form.append('my_file', fs.createReadStream('/foo/bar.jpg'));
axios.post('https://example.com', form, { headers: form.getHeaders() })
或者, 使用一个拦截器:
axios.interceptors.request.use(config => {
if (config.data instanceof FormData) {
Object.assign(config.headers, config.data.getHeaders());
}
return config;
});
应用
axios 封装
一般为了业务需要,会对 axios 进行封装,统一处理:环境配置、 默认配置、添加拦截器、请求方法封装等。
不同应用对于 axios 封装会有不同的方法,SPA 单页面应用和 SSR 服务端渲染的同构应用对于 axios 的配置不同:
- SPA 应用接口请求主要在浏览器端,无需服务端,无需区分浏览器环境和服务端;
- SSR 同构应用涉及 服务端和浏览器端接口请求,需要区分不同环境的请求。
- 服务端渲染无登录相关,请求无需 token 处理、无弹窗提示等。
封装时区分内容:
创建 axios 实例:封装 axios 时候尽量创建一个新的 axios 实例,避免引入 axios 默认实例。
原因:引入 axios 默认实,在修改 axios 默认实例的默认配置后,默认配置会影响到所有其他引入 axios 默认实例的接口。在 SPA 单页面应用中一般没什么问题,但是在同构应用中,不同客户端和服务端请求处理不同,因此使用默认引入的 axios 实例容易导致错误。
环境配置:单页面应用仅仅区分 开发/测试/生产环境,同构应用还要区分 浏览器和服务端环境。
开发/测试/生产环境:根据
process.env.NODE_ENV配置不同的baseURL,使项目只需执行相应打包命令,就可以在不同环境中自动切换请求主机地址。//单页面应用下,五服务端渲染环境时候封装方式 const getBaseUrl = (env = process.env.NODE_ENV) => { let base = { production: '/', development: 'http://localhost:3000', test: 'http://localhost:3001', }[env]; return base? base : '/' ; };浏览器和服务端环境:同构应用需要区分。根据
process.env.isServer(通过 webpack 打包时注入) 判断浏览器和 node 服务端运行环境,在浏览器和 node 服务端中,请求中 baseUrl 会略有差异:在 Node 服务器中,请求需要配置默认 baseUrl,因为服务器不知道请求域名/地址。
在浏览器中不需要配置 baseUrl,浏览器默认会使用当前页面下的域名作为 baseUrl 发送请求。(同构应用在服务端渲染时候获取初始接口数据,渲染静态化页面后进行客户端激活,客户端激活后处理客户端请求接口)
//SSR同构应用下, 服务端渲染和客户端渲染同时存在 const getBaseUrl = (env = process.env.NODE_ENV,isServer = process.env.isServer) => { let base = { production: '/', development: 'http://localhost:3000', test: 'http://localhost:3001', }[env]; return (isServer === 'server')? (base? base : '/') : '' ; };
默认配置/参数:如果是同构应用,需要区分浏览器环境和 Node 环境(服务端渲染),根据
process.env.isServer判断。浏览器环境和 Node 环境的统一配置:
- 配置超时时间 timeout 属性
仅浏览器环境下配置:
配置允许携带凭证 widthCredentials 属性设为 true 。客户端环境下添加, 服务端渲染时不需要。
添加 Token: 为了避免每次请求中手动添加 Token,可以在 header 中默认配置统一添加 token。,在 node 环境下(服务端渲染时) 不需要添加。
client.defaults.headers = { post: { "Content-Type": "application/json;charset=UTF-8", }, get "User-Token"() { return getAccessToken() //获取 token 方法 }, };
添加拦截器: 拦截器需要返回配置,否则整个请求不会进行。
可以在请求拦截器中 添加token凭证、统一设置语言、统一设置内容类型、指定数据格式、添加默认参数、loading缓冲效果等
如:请求拦截中添加请求默认参数。
//示例 client.interceptors.request.use( function (config) { // console.log(config) if (config) { if (["post", "delete", "put"].includes(config.method)) { config.data.languageCode = languageCode; config.data.countryCode = countryCode; config.data.platform = platform; } else if (config.method === "get") { config.params.languageCode = languageCode; config.params.countryCode = countryCode; config.params.platform = platform; } } return config; //返回这个配置,否则整个请求不会进行 }, function (error) { return Promise.reject({ errMsg: error || "404(TimeOut)", errCode: 404, }); } );
响应拦截器:过滤响应数据、根据状态码进行统一处理,如弹窗提示、清除 token、token过期处理、清除loading缓冲效果等。
- 注意:弹窗提示、清除 token、token过期处理等需要在浏览器端环境下,Node 环境(服务端渲染)下不需要样式和 token。( Token 是用户登录相关数据,服务端渲染时不需要用户登录)
- token 过期处理:首先刷新 token、根据结果判断,刷新失败则清除 token 、退出登录、清除用户数据;刷新成功重新保存新的 token。
请求方法封装:封装
request方法,在 request 方法上进行其他请求方法 (get、post、delete、put ...) 二次封装。不同请求方法参数不同,封装方法参数。export function post(url, data = {}, config = {}) { return request({ method: "post", url, data, config, }); } export function get(url, params = {}) { return request({ url, params, }); } export function put(url, data = {}) { return request({ method: "put", url, data, }); }
注意:
- 默认实例配置、新建实例配置、拦截器、请求方法 request 中都可以处理 默认配置、默认参数、token处理等。
- 区别: 根据配置合并策略:请求的
config参数 >(覆盖) 实例的defaults属性 > (覆盖) 库默认值。
API 管理
目前前后端开发基本采用前端分离开发模式,前端 API 管理主要为前端在业务层 API 中的划分方式。
常见采用划分方式:
- 按照 API 文档模块划分 API 模块:axios 统一封装后,按照页面/模块功能划分文件目录。
常见 API 文档管理工具:
- Swagger
- YApi
- Eolinker
- ShowDoc
- DOClever
- RAP2
MOCK 数据
在时机项目开发中,经常遇到:
- 前端开发依赖于后端接口数据,但是后台人员不足或者无法立即到位,前端迟迟不能开工;
- 前端参照 ui 设计图,完成对应的静态页面(没有数据交互),待后台人员到位,再进行二次开发,协助完成接口对接。
因此,为了解决此类困境,前端通常可以使用 mock api 方式 在前后端同时开发的时候,后端接口数据没有出来,前端可以mock假数据,模拟开发。
前端 mock 数据方法:
- 使用文档管理工具 Mock,前端代理到文档管理工具地址;
- mock 同步接口文档并使用 Mock.js 本地启动 mock 服务;
- 优点: 可以通过修改本地 mock 数据测试页面显示结果,提高开发效率;